What is Polygon (Matic Network)?
Polygon is the answer to some of the major challenges Ethereum faces such as high fees, poor user experience, and low transaction throughput.
The platform aims to create “Ethereum’s blockchain network” – that is, the multi-chain ecosystem of blockchains compatible with Ethereum. To achieve this, they offer an easy-to-use framework that allows developers to launch their own custom Ethereum-compatible blockchain with just one click.
Polygon opens up a world in which separate blockchains can freely and easily exchange value and information – removing the technological and ideological barriers that separate most blockchains today. The project was originally called the Matic Network, but was later renamed Polygon as the scope of the project was expanded. While Matic is a simple class 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, Polygon is the infrastructure for a network of collaborative blockchains, scaling up large scale and maintaining their autonomy.
Polygon’s development team?
Polygon is currently being developed by a multidisciplinary team co-founded by four people including Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun and Mihailo Bjelic. Kanani is currently the CEO of Polygon and an experienced developer with a penchant for scaling mechanisms, while the rest of the team brings a wealth of experience building, managing, and developing technology companies.
The function of Polygon (MATIC)
- Scalability: fast, low-cost and secure transactions on Matic sidechain with accuracy achieved on the main chain, and Ethereum is the first compatible layer-1 database
- High throughput: achieves up to 7000 TPS (transactions per second) on a single sidechain on the internal testnet. More chains will be added to scale horizontally
- User experience: smooth user experience. Native mobile app support and SDK with WalletConnect support.
- Security: Polygon operators are also stakers in the PoS system.
- Public sidechains: Polygon sidechain is public, has a non-licensing nature and is capable of supporting multiple protocols.
How does polygon work?
Polygon offers a variety of modules that developers can use to easily deploy and configure their own custom block chain. These include administrative and consensus modules, as well as multiple virtual machine execution and deployment environments.
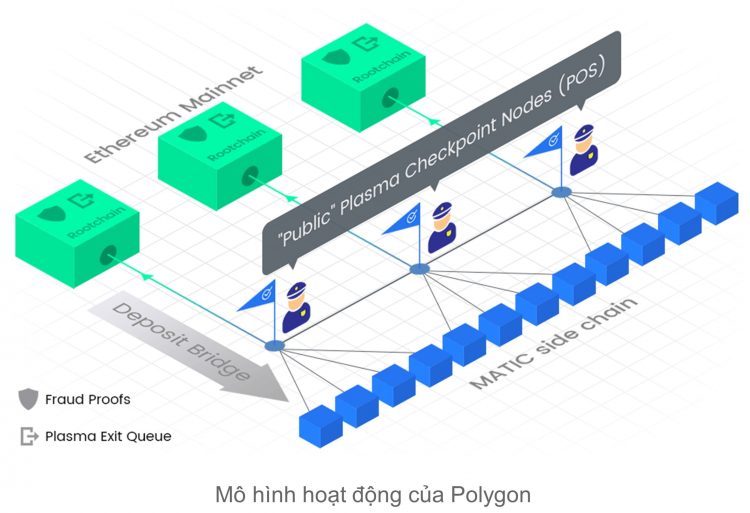
Blockchains launched in this way are configured to benefit from Matic’s proof-of-stake (PoS) sidechain, which uses networks of validators to dramatically speed up transactions and cut fees to a minimum – while perfecting everything on the Ethereum main chain.
Polygon supports two types of chains: standalone chains and secure chains. Standalone chains are sovereign blockchains that are directly compatible with Ethereum, while security chains simply launch their security by leveraging a network of professional validators.
At first, all independent chains in the Polygon ecosystem will be Matic PoS chains, but other party chains and business chains will be supported with later updates.
The platform is designed to support a variety of blockchain scaling mechanisms, including Matic Plasma, zk Rollups, Optimistic Rollups and Validum – all designed to enhance the transaction volume of link blockchains without compromising security or user experience. Polygon only supports Matic Plasma scaling solution. This basically works by offloading transactions from the Ethereum main chain into Polygon’s Matic PoS chain, before perfecting everything on the main chain. In the future, Polygon will support various alternative scale scaling solutions to give developers the freedom to choose the solution that best suits their needs.
Despite being rebranded, the polygon network’s original utility token is still called Matic. This is largely used to pay gas fees and participate in administration, while also being used throughout the rapidly expanding Polygon DeFi ecosystem.
Advantages of Polygon:
- The ability to process transactions quickly: By using a consensus mechanism that completes the process of confirming a transaction in a single block, Polygon can maintain a fast transaction processing speed. Polygon’s average processing time is 2.1 seconds.
- Transaction fees are always low: Polygon keeps fees low, with regular transaction fees of around $0.01
Disadvantages of Polygon:
- Not an autonomous blockchain: Polygon is a Class 2 solution that works on the Ethereum platform. If the Ethereum platform is severely disrupted or no longer exists, then Polygon will likely lose value.
- Limited use cases for Matic: Matic tokens are designed to manage and secure the Polygon platform and pay transaction fees. Unlike some digital currencies, Matic is not usually used for everyday purchases.
Polygon and Ethereum Comparison

Polygon is a compatible and complementary secondary scale scaling solution to the Ethereum blockchain. Polygon aims to improve Ethereum as a blockchain development network. Polygon complements Ethereum by providing additional features related to blockchain sovereign security, user experience, and developer experience. Ethereum is currently using the PoW proof-of-work consensus mechanism and is gradually moving to use PoS equity proof. Polygon uses a modified proof-of-stake mechanism that allows for quick and cheap processing of transactions.
What is a Matic coin?
MATIC coin is the official token of Polygon Network. It is a coin developed according to the ERC20 standard, used as the currency of the Polygon network, which is mainly used to pay gas fees, or contribute to the security of the network through betting. Parameters of Matic coin: Token Name : Polygon Copper Code: MATIC Blockchain: Ethereum, Polygon Standard Token: ERC-20 Contract: 0x7d1afa7b718fb893db30a3abc0cfc608aacfebb0 Token Type: Utility (Utility) Total Supply: 10,000,000,000 MATIC Total Circulation: 6,872,890,164